Software Testing
Definisjoner
- Unit testing
- Integration testing
- System testing
- Systemintegrasjonstesting
- End-to-end testing (verdikjedetesting)
- Funksjonell vs. ikke-funksjonell testing
- White box vs. black box testing
- Regresjonstesting
- TDD - Testdrevet utvikling
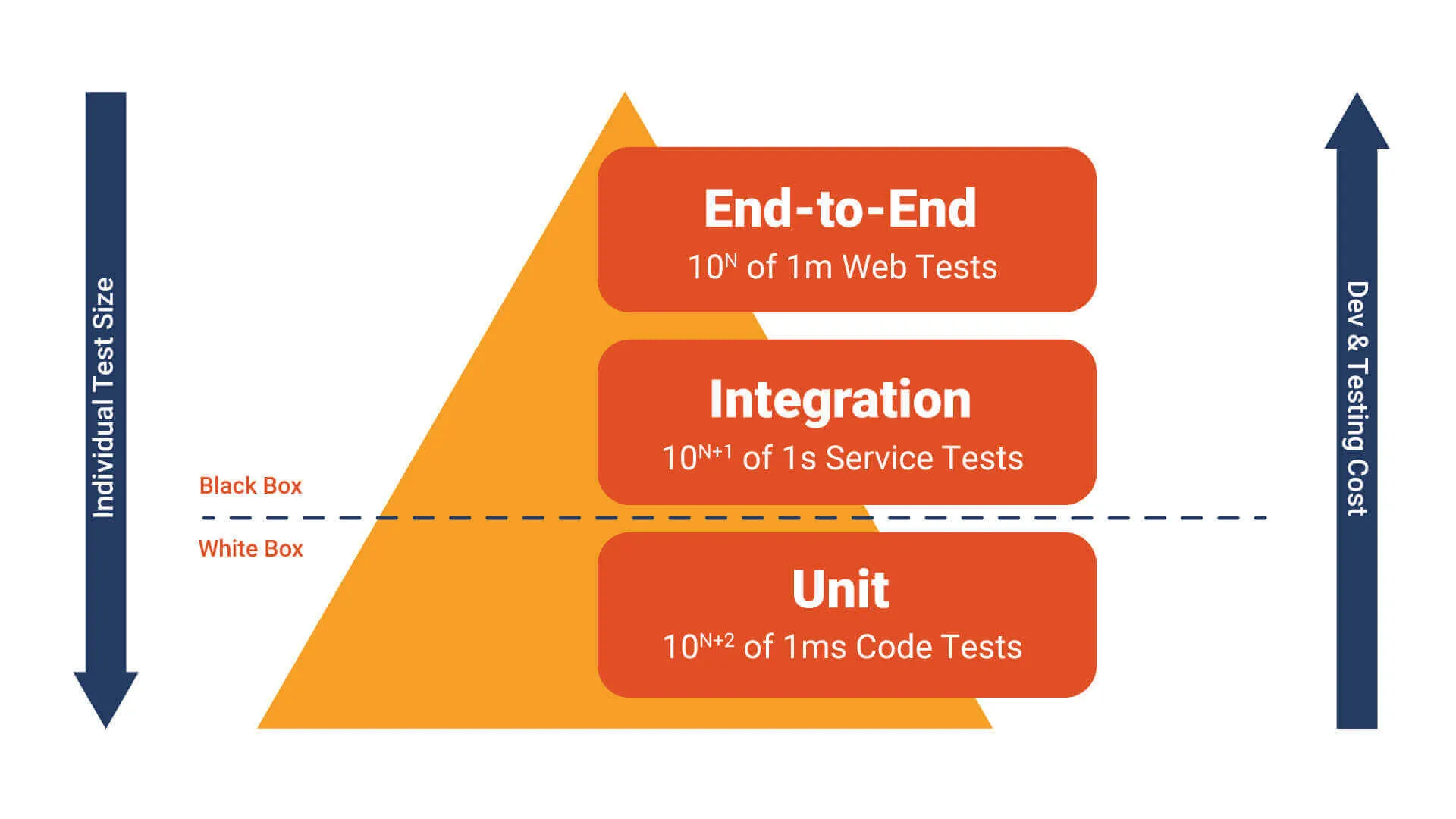
Unit testing
- Happy path
- Edge case
- Corner case

Hvorfor skrive enhetstester?
- Sikre at koden funger nå
- Sikre at koden funker i fremtiden, at ikke nye eller gamle bugs (re)introduseres (regresjonstesting)
- Raskere refaktorering
- Dokumentasjon!
- En anledning til å tenke gjennom hvordan koden oppfører seg i litt uvanlige situasjoner (edge cases)
- En anledning til å tenke igjennom om interfacet er godt (TDD)
"Testing our code works how we expect is only one side of the coin, of course. For more confidence in our code, we must also show that it doesn't work how we don't expect, so that bad actors or incorrect usage is handled correctly"
Men jeg vet at koden min funker
def triple(x: float) -> float:
return x * 3
def test_triple_happy_path():
assert triple(2.0) == 6.0
# PASSED
def triple(x: float) -> float:
return x * 3
def test_triple_happy_path():
assert triple(2.0) == 6.0
# PASSED
def test_triple_floating_point_error():
assert triple(0.1) == 0.3
# FAILED
# 0.30000000000000004 != 0.3
def test_triple_large_float():
f = 1.0e308
assert triple(f) == triple(int(f))
# FAILED
# inf != 300000000000000003293...
Oppgave
from typing import Sequence, TypeVar
import pytest
T = TypeVar("T")
def first(seq: Sequence[T]) -> T:
"""Return the first element of the provided sequence."""
return seq[0]
def test_first_happy_path():
assert first([1, 2, 3]) == 1
# PASSED
from typing import Sequence, TypeVar
import pytest
T = TypeVar("T")
def first(seq: Sequence[T]) -> T:
"""Return the first element of the provided sequence."""
return seq[0]
def test_first_happy_path():
assert first([1, 2, 3]) == 1
# PASSED
def test_first_empty():
with pytest.raises(IndexError):
first([])
# PASSED
Oppgave
def last(it: Iterator[T]) -> T:
"""Return the last element of the provided iterator."""
for item in it:
pass
return item
def test_last_with_generator():
def count_to_three():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
assert last(count_to_three()) == 3
# PASSED
def last(it: Iterator[T]) -> T:
"""Return the last element of the provided iterator."""
for item in it:
pass
return item
def test_last_with_generator():
def count_to_three():
yield 1
yield 2
yield 3
assert last(count_to_three()) == 3
# PASSED
def test_last_empty():
assert last(iter([])) is None
# FAILED
# UnboundLocalError: cannot access local variable 'item' where it is not associated with a value
def test_last_with_infinite_iterator():
from itertools import cycle
infinite_iterator = cycle([1, 2, 3])
assert last(infinite_iterator) is None
# Function call never returns
Oppgave
def sum_diff_ratio(a: int | float, b: int | float) -> float:
return (a + b) / (a - b)
def test_sum_diff_ratio_happy_path():
assert sum_diff_ratio(1, 2) == -3
# PASSEDdef sum_diff_ratio(a: int | float, b: int | float) -> float:
return (a + b) / (a - b)
def test_sum_diff_ratio_happy_path():
assert sum_diff_ratio(1, 2) == -3
# PASSED
def test_sum_diff_ratio_division_by_zero():
with pytest.raises(ZeroDivisionError):
sum_diff_ratio(2, 2)
# PASSEDOppgave
def linspace(n: int) -> list[float]:
"""Returns a list of n equidistant values in the closed interval [0, 1]."""
return [i / (n - 1) for i in range(n)]
def test_linspace_happy_path():
assert linspace(3) == [0.0, 0.5, 1.0]
# PASSEDdef linspace(n: int) -> list[float]:
"""Returns a list of n equidistant values in the closed interval [0, 1]."""
return [i / (n - 1) for i in range(n)]
def test_linspace_happy_path():
assert linspace(3) == [0.0, 0.5, 1.0]
# PASSED
def test_linspace_zero():
assert linspace(0) == []
# PASSED
def test_linspace_one():
assert linspace(1) == [0.5]
# FAILED
# ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
def test_linspace_negative():
with pytest.raises(ValueError):
assert linspace(-5) == []
# FAILED
# DID NOT RAISE <class 'ValueError'>Oppgave
def load_csv(csv_file: Path) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Load a CSV file into a dataframe and select the integer columns a, b, and c."""
return (
pd.read_csv(csv_file)
.convert_dtypes(infer_objects=True)
.select_dtypes(int)
.loc[:, ["a", "b", "c"]]
)
def test_load_csv_happy_path(tmp_path):
csv_file = tmp_path / "test.csv"
csv_file.write_text("a,b,c\n 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 \n 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 \n")
expected = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], columns=["a", "b", "c"], dtype="Int64")
actual = load_csv(csv_file)
pd.testing.assert_frame_equal(actual, expected)
# PASSED
def load_csv(csv_file: Path) -> pd.DataFrame:
"""Load a CSV file into a dataframe and select the integer columns a, b, and c."""
return (
pd.read_csv(csv_file)
.convert_dtypes(infer_objects=True)
.select_dtypes(int)
.loc[:, ["a", "b", "c"]]
)
def test_load_csv_happy_path(tmp_path):
csv_file = tmp_path / "test.csv"
csv_file.write_text("a,b,c\n 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 \n 4.0, 5.0, 6.0 \n")
expected = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], columns=["a", "b", "c"], dtype="Int64")
actual = load_csv(csv_file)
pd.testing.assert_frame_equal(actual, expected)
# PASSED
def test_load_csv_empty(tmp_path):
csv_file = tmp_path / "test.csv"
csv_file.write_text("")
expected = pd.DataFrame()
actual = load_csv(csv_file)
pd.testing.assert_frame_equal(actual, expected)
# FAILED
# pandas.errors.EmptyDataError: No columns to parse from file
def test_load_csv_dtype_inference(tmp_path):
csv_file = tmp_path / "test.csv"
csv_file.write_text("a,b,c\n 1.0, 2.0, 3.0 \n 4.5, 5.0, 6.0 \n")
expected = pd.DataFrame([[1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]], columns=["a", "b", "c"], dtype="Int64")
actual = load_csv(csv_file)
pd.testing.assert_frame_equal(actual, expected)
# FAILED
# KeyError: "['a'] not in index"
Oppgave
def consumption_imbalance_distributor(imbalance: pd.Series, nodes: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.Series:
"""Distribute bidzone imbalance to nodes based on their share of the bidzone consumption."""
fraction = nodes["P"] / nodes.groupby("bidzone")["P"].transform(sum)
return pd.Series(fraction * imbalance.loc[nodes["bidzone"]].values, index=nodes.index)
def test_consumption_imbalance_distributor_happy_path():
imbalance = pd.Series(
data=[10.0, 12.0, -6.0],
index=pd.Index(["NO1", "NO2", "SE1"], name="bidzone")
)
nodes = pd.DataFrame(
{
"bidzone": ["NO1", "NO2", "NO2", "NO2", "SE1", "SE1"],
"P": [1.0, 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, 1.0, 2.0],
},
)
expected = pd.Series([10.0, 2.0, 4.0, 6.0, -2.0, -4.0], name="P")
actual = consumption_imbalance_distributor(imbalance, nodes)
pd.testing.assert_series_equal(actual, expected)
# PASSEDdef consumption_imbalance_distributor(imbalance: pd.Series, nodes: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.Series:
"""Distribute bidzone imbalance to nodes based on their share of the bidzone consumption."""
fraction = nodes["P"] / nodes.groupby("bidzone")["P"].transform(sum)
return pd.Series(fraction * imbalance.loc[nodes["bidzone"]].values, index=nodes.index)
def test_consumption_imbalance_distributor_denominator_zero():
imbalance = pd.Series(
data=[6.0],
index=pd.Index(["SE1"], name="bidzone")
)
nodes = pd.DataFrame(
{
"bidzone": ["SE1", "SE1"],
"P": [-5.0, 5.0],
},
)
expected = pd.Series([3.0, 3.0], name="P")
actual = consumption_imbalance_distributor(imbalance, nodes)
pd.testing.assert_series_equal(actual, expected)
# FAILED
# [left]: [-inf, inf]
# [right]: [3.0, 3.0]Oppgave
def frequency_distribution(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.Series:
"""Return a series with the frequency of each value in the given dataframe.
Args:
df: A dataframe with a single column.
"""
return df.squeeze().value_counts().sort_index()
def test_frequency_distribution_happy_path():
df = pd.DataFrame([1, 2, 2, 2, 3], columns=["a"])
expected = pd.Series(
index=pd.Index([1, 2, 3], name="a"),
data=[1, 3, 1],
)
actual = frequency_distribution(df)
pd.testing.assert_series_equal(actual, expected, check_names=False)
# PASSEDdef frequency_distribution(df: pd.DataFrame) -> pd.Series:
"""Return a series with the frequency of each value in the given dataframe.
Args:
df: A dataframe with a single column.
"""
return df.squeeze().value_counts().sort_index()
def test_single_col_df_to_series_empty():
df = pd.DataFrame()
expected = pd.Series()
actual = frequency_distribution(df)
pd.testing.assert_series_equal(actual, expected, check_names=False)
# FAILED
# [left]: int64
# [right]: object
def test_single_col_df_to_series_single_row():
df = pd.DataFrame([1], columns=["a"])
expected = pd.Series([1])
actual = frequency_distribution(df)
pd.testing.assert_series_equal(actual, expected, check_names=False)
# FAILED
# 'numpy.int64' object has no attribute 'value_counts'Oppgave
@decorators.time_logger(logger=logger)
def run_opf_scenarios(
case: CaseOpf,
scenarios: pd.DataFrame,
afrr: tuple[pd.DataFrame, pd.DataFrame],
infeasible_threshold: float,
station_group_names: dict | None = None,
) -> ScenarioResults:
"""Solve the optimization problem for all scenarios and evaluate the bid activations.
Args:
case: Case
scenarios: Flow on the border for all scenarios
bids: Bids
afrr: Tuple of aFRR down and aFRR up capacities by station group and bidzone
ptc: Power transfer corridor description
infeasible_threshold: Threshold for fraction of infeasible scenarios, abort run if exceeded
station_group_names: dict mapping station group IDs to station group names
Returns: Classified bids from scenarios
"""
up_down = cycle(("up", "down"))
afrr_directions = pd.Series(islice(up_down, len(scenarios.columns)), index=scenarios.columns)
sensitivites = sensitivity_injection(case, "quantity")
results = ScenarioResults(case, scenarios.columns, sensitivites)
p_origin = case.load["p"].copy()
afrr_down, afrr_up = _get_generators_adjusted_with_afrr(case.gen, afrr, station_group_names)
for nr, direction in afrr_directions.items():
distributed_consumption = consumption_imbalance_distributor(
scenarios[nr], case.load, case.bus["ide"]
)
case.load.loc[:, "p"] += distributed_consumption
case.gen["p"] = afrr_up["p"] if direction == "up" else afrr_down["p"]
case.opf_update_injections()
case.solve()
results.evaluate_scenario(nr, case)
case.load.loc[:, "p"] = p_origin
if fraction_infeasible := round(results.fraction_infeasible, 2) > 0:
logger.info(f"Fraction of infeasible scenarios: {fraction_infeasible}.")
if fraction_infeasible >= infeasible_threshold:
raise Exception(
f"Run aborted because the fraction of infeasible scenarios ({fraction_infeasible})"
f" exceeds the threshold ({infeasible_threshold}."
)
results.evaluate_purpose()
results.calculate_sysact_volumes()
results.set_sensitive_status()
return resultsOppsummering / sjekkliste
Vurder å teste følgende
- På grensen av et definert intervall
- Utenfor grensen til et definert intervall
- 0
- 1
- Negative verdier
- nan og inf
- Forventede verdier mangler (dict uten forventet nøkkel, DataFrame uten forventet kolonne)
- Tomme verdier eller null-verdier ("", [], None)
- Uventede typer. DF med uventede dtypes.
- Forventede exceptions
- Hvis concurrent / parallel programming: Locks, timing
For alle punktene over, gjelder følgende: Ikke bare test med grenseverdier som funksjonsargumenter. Tenke også på hvilke omstendigheter som kan føre til at grenseverdier dukker opp underveis.
Hypothesis
Hypothesis
from hypothesis import given
from hypothesis import strategies as st
def test_sorted_happy_path():
assert sorted([3, 1, 2]) == [1, 2, 3]
# PASSED
@given(st.lists(st.integers()))
def test_sorted_each_element_greather_than_the_last(lst):
lst_sorted = sorted(lst)
for i in range(len(lst_sorted) - 1):
assert lst_sorted[i] <= lst_sorted[i + 1]
# PASSED
from hypothesis import given
from hypothesis import strategies as st
def test_sorted_happy_path():
assert sorted([3, 1, 2]) == [1, 2, 3]
# PASSED
@given(st.lists(st.integers()))
def test_sorted_each_element_greather_than_the_last_ints(lst):
lst_sorted = sorted(lst)
for i in range(len(lst_sorted) - 1):
assert lst_sorted[i] <= lst_sorted[i + 1]
# PASSED
@given(st.lists(st.floats()))
def test_sorted_each_element_greather_than_the_last_floats(lst):
lst_sorted = sorted(lst)
for i in range(len(lst_sorted) - 1):
assert lst_sorted[i] <= lst_sorted[i + 1]
# FAILED
# 0.0 != nanHypothesis
import hypothesis.strategies as st
from hypothesis import given
def sum_diff_ratio(a: int | float, b: int | float) -> float:
return (a + b) / (a - b)
int_or_float = st.one_of(
st.integers(),
st.floats(allow_nan=False, allow_infinity=False)
)
@given(a=int_or_float, b=int_or_float)
def test_sum_diff_ratio_property(a, b):
result = sum_diff_ratio(a, b)
assert isinstance(result, float)
# FAILED
# ZeroDivisionError: division by zero
# Falsifying example: test_sum_diff_ratio_property(
# a=0,
# b=0,
# )Hypothesis
from math import e, pi
from hypothesis import given, settings
from hypothesis import strategies as st
def some_calculation(x):
return (x + e) / (x - pi)
def test_some_calculation_edge_case():
assert some_calculation(pi)
# FAILED
# ZeroDivisionError: float division by zero
@given(x=st.floats())
@settings(max_examples=1000)
def test_some_calculation(x):
some_calculation(x)
# PASSEDQ: Så man trenger egentlig ikke å manuelt skrive edge case-tester?
A: Jo, dessverre ...
Slutt
presentasjon: